The numerous techniques of TELEVISION transmission
Programming broadcast is the transmission of television terminals' programs (often called networks) that is usually directed to a certain audience.
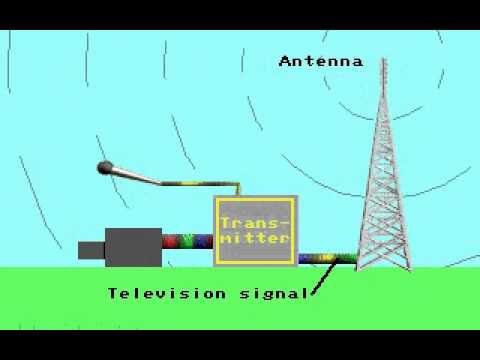
ANALOGUE TERRESTRIAL TELEVISION
Earthbound television is a term which describes settings of television broadcasting which do not involve satellite transmission or through underground cords.
Terrestrial tv broadcasting go back to the very starts of television as a medium itself and also there was essentially nothing else method of television delivery till the 1950s with the starts of cable television service, or community antenna television (CATV).
The initial non-terrestrial method of supplying television signals that in no other way depended upon a signal originating from a typical terrestrial resource began with using interactions satellites throughout the 1960s and 1970s of the twentieth century.
Analogue TELEVISION encodes the picture and audio info and also sends them as an analogue signal in which the message sent by the broadcasting signal is composed of amplitude and/or regularity variations as well as modulated into a VHF or UHF service provider.
The analogue television photo is "attracted" numerous times on the screen (25 in BUDDY system) as a whole each time, as in a motion picture film, regardless of the web content of the picture.
ELECTRONIC SATELLITE TV
Satellite tv is tv signals supplied using communications satellites as well as obtained by dish antenna and also set-top boxes. In many areas of the world it gives a variety of networks and solutions, typically to areas that are not serviced by terrestrial or cable providers.
Satellite tv, like various other communications passed on by satellite, begins with a transmitting antenna located at an uplink facility which have large live tv online uplink dish antenna, as long as 9 to 12 meters (30 to 40 feet) in size what cause more accurate intending as well as increased signal stamina at the satellite.
The uplink dish is sharp towards a details satellite and also the uplinked signals are transmitted within a particular frequency range, so regarding be gotten by one of the transponders tuned to that frequency array aboard that satellite, which 'retransmits' the signals back to Earth but at a different regularity band, a process referred to as "translation", utilized to prevent interference with the uplink signal, typically in the C-band (4-- 8 GHz) or Ku-band (12-- 18 GHz) or both.
The downlinked satellite signal, quite weak after taking a trip the great distance, is accumulated by an allegorical obtaining recipe, which reflects the weak signal to the meal's centerpiece where is a "downconverter" device called LNB (low-noise block) that is essentially a waveguide that gathers the signals, intensifies the relatively weak signals, filterings system the block of frequencies in which the satellite TV signals are sent, and converts it to a reduced regularity range in the L-band array.
The evolution of LNB was a need, so the layouts for microstrip based converters were adapted for the C-Band making the most of its central style that was the concept of a block for down conversion of a variety of regularities to a reduced, and also technically a lot more quickly handled block of frequencies, the IF - intermediate frequency.
The benefits of using an LNB are that less costly cord could be made use of to link the indoor receiver with the satellite TV meal as well as LNB, and that the innovation for dealing with the signal at L-Band as well as UHF was much less costly than that for handling the signal at C-Band frequencies.
The shift to less costly technology from the 50 Ohm insusceptibility wire as well as N-Connectors of the very early C-Band systems to the 75 Ohm technology and also F-Connectors allowed the early satellite TELEVISION receivers to utilize what were in truth modified UHF TV receivers which selected the satellite television channel for down conversion to an additional reduced intermediate frequency centered on 70 MHz where it was demodulated. This shift allowed the satellite television industry to transform to an even more business automation one.
The satellite receiver demodulates and also converts the signals to the wanted form (outputs for tv, audio, information, and so on) as well as sometimes, the receiver consists of the capacity to unscramble or decrypt; the receiver is after that called an Integrated Receiver/Decoder or IRD.
CABLE TV
Cable Television Service or Community Antenna Television (CATV) is a system for circulation of audiovisual web content for television, FM radio and other solutions to customers via fixed coaxes, staying clear of the standard system of radio broadcasting antennas (program tv) and also have extensive use, mostly through the pay-TV services.
Technically, the cable TV includes the distribution of a variety of tv networks obtained and also processed in a main area (known as head-end) to subscribers within a neighborhood with a network of optical fiber and/or coaxes as well as broadband amplifiers.
Using different frequencies allows many channels to be dispersed with the very same cable, without separate cords for each, and also the receiver of the TELEVISION or Radio chooses the desired network from among all transferred.
A cable television service system begins at the head end, where the program is gotten (as well as occasionally stemmed), magnified, and then transmitted over a coaxial cable network.
ELECTRONIC TERRESTRIAL TELEVISION
Digital Terrestrial Television (DTTV or DTT) is an implementation of digital television innovation to give a majority of networks and/or far better top quality of picture as well as sound using airborne broadcasts to a standard antenna (or aerial) instead of a satellite dish or cable television connection.
The modern technology used in Europe is DVB-T that is unsusceptible to multipath distortion.
DTTV is transferred on superhigh frequency through the airwaves that resemble conventional analogue tv, with the main distinction being making use of movie theater transmitters to allow function of several networks on a solitary frequency array (such as a UHF or VHF network).
The amount of information that can be transmitted (as well as as a result the number of channels) is straight influenced by the inflection technique of the channel.
The modulation technique in DVB-T is COFDM with either 64 or 16 state Quadrature Amplitude Inflection (QAM). Generally a 64QAM network is capable of sending a higher bit price, yet is a lot more vulnerable to disturbance. 16 as well as 64QAM can be incorporated in a single manifold, supplying a controlled deterioration for more crucial program streams. This is called hierarchical inflection.
New developments in compression have caused the MPEG-4/ AVC criterion which will certainly enable 2 hd services to be coded into a 24 Mbit/s European earthbound transmission network.
WEB TELEVISION
Web TELEVISION, TVIP, or TV on the web is the transmission of a programs grid through the Web. It can be recognized "regular" TELEVISION channels or channels specifically designed for the Web.
Internet TELEVISION, in a streamlined type, is absolutely nothing greater than the provision of video clip and also audio online; and the way to assist the transmission varies from the screen of a computer system through making use of an iPod or a smart phone to the TV set if one have the decoder.
